Let’s face it–no one enjoys the hassle of printing, signing, scanning, and emailing documents back and forth. It’s time-consuming and a bit outdated in today’s work world, with more remote teams and digital communication.
That’s where electronic signatures come in. Whether you’re finalizing a contract, approving an invoice, or onboarding a new hire, electronic signatures offer a way to get things done quickly and securely without ever touching a piece of paper.
What is an electronic signature, and how does it differ from signing a traditional paper document? If you’ve ever clicked “I agree” online or signed something digitally, you’ve already used one. However, there’s a lot more going on behind the scenes to make sure that electronic signatures are legally binding, secure, and recognized across the globe.
In this article, we’ll dive into how electronic signatures work, why they’re trusted, and how they can save time and energy. By the end, you’ll know exactly why they’ve become the go-to choice for businesses and individuals when signing important documents.
What is an Electronic Signature?
An electronic signature, or e-signature, is a digital way of agreeing to a document’s conditions. At its core, it’s a method of signing something electronically rather than with pen and paper. It’s often how contracts are signed in modern business practices.
Whether you’re clicking an “I Agree” button, typing your name into a signature box, or drawing your signature with your finger on a mobile device, these all count as electronic signatures.
What makes them unique is that they don’t just capture a symbol of your name; they also come with built-in security measures to verify that it was you who signed the document.
The Practicality of Electronic Signatures in Business
In legal terms, electronic signatures are recognized under laws like the ESIGN Act in the U.S. and eIDAS in the European Union. These laws ensure that electronic signatures carry the same weight as traditional “wet” signatures as long as they meet certain criteria, such as being tied to an identifiable individual and used with the intent to sign a record.
This makes them a practical and secure alternative for nearly every situation requiring a signature. That includes business contracts, job offers, workplace agreements, invoices, and more.
Does an Electronic Signature Need to Resemble Your Handwritten Signature?
An e-signature doesn’t have to resemble a handwritten signature to be legal and enforceable. As long as the signature is applied with the intent to sign and is linked to the document, it’s valid. For example, clicking a box that says “I Agree” is legally recognized as a signature in many cases.
Send Documents for eSignature
With just a few clicks, without leaving your inbox
How Do Electronic Signatures Work?
Electronic signatures work by capturing the intent to sign a document in a secure and traceable way. While it might seem like a simple click or a typed name, much more is happening behind the scenes to ensure the signature is valid and legally binding.
When you electronically sign a document, the system creates a unique digital record that links the signature to the document and the person signing it. This record often includes metadata such as the date, time, IP address, and email address, ensuring authenticity and security.
The process typically starts with the sender uploading a document that requires a signature. This document can be in formats like PDF or Word, and once uploaded, it’s sent via email to the recipient for signing.
The recipient receives a link to the document, where they can review it, sign it electronically, and then send it back. The signature can take the form of a drawn signature, typed name, or even a simple “I Agree” checkbox, depending on the platform being used.
Efficiency of Electronic Signatures
Sending documents through email for electronic signatures has become one of the most efficient ways to get agreements signed quickly. Whether you’re working with contracts, invoices, or employment forms, the ability to email a document for signature eliminates the need for printing and scanning, saving time and effort for everyone involved.
Once the document is signed, both the sender and recipient receive a confirmation, and the completed document is securely stored for future reference. The use of tracking features further enhances transparency, allowing all parties to know exactly when the document was signed and by whom.
Legal Validity and Compliance
As we mentioned earlier, electronic signatures are more than just convenient. They’re also legally binding in most parts of the world.
In the U.S., for example, the Electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce (ESIGN) Act was passed in 2000. It established that electronic signatures carry the same legal weight as traditional handwritten ones as long as certain conditions are met. Those conditions include the expressed consent for an e-signature from everyone involved and the ability to verify who the signer is and the intent to sign.
Similarly, most U.S. states have adopted the Uniform Electronic Transactions Act (UETA) to reinforce this. These laws ensure that electronic signatures are recognized and enforceable across various industries and types of documents.
Internationally, the European Union’s eIDAS regulation governs electronic signatures, ensuring they are legally valid throughout EU member states. Many other countries have adopted similar frameworks to establish the legal status of e-signatures.
As a result, businesses worldwide can confidently use electronic signatures to complete agreements, knowing they comply with global standards.
Instances Where E-Signatures Might Not be Valid
There are still some documents and situations where electronic signatures might not be valid. For example, certain family law documents, like wills or marriage certificates, often require a handwritten signature for legal reasons. It’s always a good idea to check the specific legal requirements in your jurisdiction for the type of document you’re signing.
Tracking E-Signatures to Ensure Compliance
A key reason why electronic signatures hold up in court is the robust security and authentication measures that back them. Unlike a simple handwritten signature, an electronic signature can be traced back to the signer using metadata like IP addresses, email addresses, timestamps, and device information.
This built-in tracking provides greater security and makes it easier to verify the authenticity of a signature if it’s ever challenged.
Tools that include tracking and verification features are essential for businesses concerned about compliance. These tools allow businesses to maintain an audit trail, clearly showing when the document was sent, signed, and by whom. This kind of tracking is not only useful for legal compliance but also for internal accountability and transparency.
Of course, with any digital tool, security, and legal compliance are ongoing concerns. Many people ask, “Is email tracking legal and safe?” when using these systems for electronic signatures. In most cases, the answer is yes, as long as you have the expressed consent of the recipient to send them a signable document, provide your contact information in the email, and include a clear unsubscribe mechanism allowing them to opt out of future emails.
Types of Electronic Signatures
Not all electronic signatures are created equal. Electronic signatures come in different forms depending on the level of security and authentication required.
The three main types are:
- Simple electronic signatures (SES)
- Advanced electronic signatures (AES)
- Qualified electronic signatures (QES)
Each serves different purposes based on the level of trust needed for the document. Let’s review each one in more detail.
Simple Electronic Signatures (SES)
The most basic form of e-signature, SES, includes:
- Typing your name
- Clicking “I Agree”
- Pasting an image of your handwritten signature into a document
These are often used in everyday transactions like signing up for services or agreeing to terms and conditions. While convenient, SES provides the least amount of security and verification, making it best suited for low-risk agreements.
Advanced Electronic Signatures (AES)
AES offers a higher level of security by linking the signature to the signer through digital certificates and encryption. To create an AES, the signer must provide proof of their identity, and the signature is cryptographically bound to the document.
AES is used for situations that require more verification, such as legal agreements or financial transactions. These signatures can’t be tampered with, adding an extra layer of trust.
Qualified Electronic Signatures (QES)
QES represents the highest level of trust and security. In addition to the requirements of AES, QES must be created with a certificate issued by a trusted certification authority, which verifies the signer’s identity.
In many countries, QES is recognized as legally equivalent to a handwritten signature, making it ideal for high-stakes transactions like real estate deals or government contracts.
How to Choose the Right Type of E-Signature
Choosing the right type of electronic signature depends on the nature of the document and the level of security you need. SES is often sufficient for routine, low-risk transactions. However, AES or QES provide the added assurance of identity verification and legal recognition for more critical agreements.
Benefits of Using Electronic Signatures
The shift to electronic signatures offers more than just convenience. Whether you’re a small business owner, a freelancer, or part of a large corporation, the benefits of using e-signatures extend across efficiency, security, cost savings, and even environmental impact.
Increased Efficiency
A big advantage of electronic signatures is the time saved. With traditional paper signatures, documents must be printed, signed, scanned, and emailed back. It can be even worse if they must be sent through physical mail, which can add days to the process.
Electronic signatures eliminate these steps, allowing documents to be signed in minutes, no matter where the signer is located. This can speed up workflows considerably, helping businesses close deals or approve agreements faster.
Additionally, real-time notifications when a document is signed through email ensure that everyone stays informed, further boosting productivity without waiting for manual updates. This is similar to how real-time email notifications keep you on top of important tasks in your inbox.
Enhanced Security
Unlike handwritten signatures, which can be forged or altered, electronic signatures come with built-in layers of security. These include digital certificates, encryption, and audit trails, all verifying the signature’s authenticity.
When a document is signed electronically, information like the signer’s IP address, timestamp, and device is logged. This makes it difficult to dispute the legitimacy of a signature, providing businesses with peace of mind, especially when dealing with sensitive agreements.
If the document is ever called into question, a digital record can be pulled to show exactly when and how it was signed.
Cost Savings
Another key benefit of e-signatures is the reduction in overhead costs. The need for paper, ink, and postage is greatly diminished when everything is done electronically.
Additionally, businesses save on storage space for physical documents, which can pile up over time. The savings might seem small on a per-document basis, but these costs add up quickly for businesses that regularly deal with contracts, invoices, or agreements.
By adopting electronic signatures, companies can reduce reliance on physical resources and allocate those savings elsewhere.
Environmental Impact
Speaking of reducing reliance on physical resources, electronic signatures are much better for the environment. Businesses can reduce waste and carbon emissions by minimizing paper use and eliminating the need for postal deliveries. It’s a small step, but adds up when considering the number of documents that change hands daily.
Mobility and Flexibility
With electronic signatures, documents can be signed anytime, anywhere.
Whether you’re on a laptop at the office, a tablet at home, or even a mobile device while on the go, e-signatures give you the flexibility to manage important agreements without being tethered to a specific location.
This is particularly useful for remote teams or international deals, so physical distance is no longer a barrier to getting signatures on time.
Common Use Cases for Electronic Signatures
Electronic signatures have become a part of countless business and personal transactions, offering a faster and more secure way to sign documents. Here are some common scenarios where you might use them:
Time Sensitive Documents
Some common use cases include contracts, sales agreements, NDAs, and invoices, where time-sensitive signatures are often required. Instead of waiting days or weeks for physical copies to be signed and returned, electronic signatures allow these documents to be signed and shared instantly.
Employment Paperwork
Another key scenario for electronic signatures is employment paperwork, such as offer letters and onboarding forms. HR teams frequently use e-signatures to streamline the hiring process, enabling new employees to review and sign documents before their first day.
Purchase Orders
Vendors and service providers use electronic signatures for contracts and purchase orders. It ensures agreements are finalized quickly, even if multiple parties are involved.
Everyday Scenarios
Electronic signatures also benefit everyday scenarios. Whether you’re agreeing to terms and conditions or signing a document to authorize a bank transfer, the convenience of electronic signatures saves time and reduces hassle.
The Best File Type for E-Signatures During These Scenarios
A popular choice for these transactions is using signable PDFs. Following email attachment best practices, PDFs are some of the safest documents to send and open since they’re simple files that are hard to tamper with or attach viruses to. This makes them ideal for legal and business documents that require secure signatures.
How to Send a Signable PDF with Mailsuite
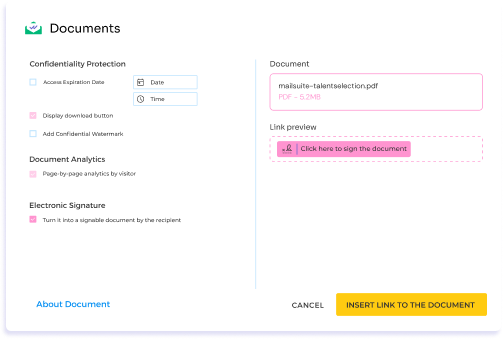
Mailsuite makes sending a PDF for electronic signatures directly from your email easy. With just a few simple steps, you can ensure that your documents are signed quickly and securely without ever leaving your Gmail inbox.
To send a signable PDF:
- Start by composing a new email in Gmail.
- Click the Mailsuite button within the email window and select the “Document for Signing” option.
- Once selected, you can browse for the PDF you need signed and attach it to the email.
- Hit “Send” once your message is complete and ready to go.
The recipient will receive a link to the PDF that allows them to easily review the document and add their electronic signature. When the recipient opens the PDF, they’ll be prompted to sign by drawing their signature, typing their name, or using a pre-configured signature. After signing, the recipient can simply confirm and send the document back to you.
Mailsuite will automatically track the entire process, recording when the document was opened, signed, and returned, giving you complete visibility. One of the best features of Mailsuite’s signable PDFs is the real-time notifications, letting you know exactly when a signature is completed.
Use Mailsuite to Simplify the Electronic Signature Process
If you want to optimize electronic signature management, Mailsuite can simplify the process.
Mailsuite offers features like inserting a document for signing and PDF Attachment eSignature. With these tools, you can send and sign important documents directly from Gmail while tracking the entire process in real-time.
Plus, with Mailsuite’s E-Signature Audit Trail, you’ll have a detailed record of every step taken during the signing process, ensuring compliance and security.
Explore Mailsuite today to see how it can streamline your workflow and keep your document signing process efficient and secure.

Send PDFs for signature straight from your email
Send, sign, and track documents effortlessly
